复杂基质中痕量目标成分的检测主要依赖于样品前处理对基质成分进行吸附净化。目前常用的样品前处理方法主要包括固相萃取(SPE)[6]、凝胶渗透色谱法(GPC)[7]、液-液微萃取[8]、超临界流体萃取(SFE)[9]等。在这些方法中,基于分散固相萃取(d-SPE)的QuEChERS方法[10]已广泛用于复杂样品前处理。在该技术中,关键组成是吸附净化剂。其中,经典的吸附剂包括乙二胺-N-丙基硅烷(PSA),石墨炭黑(GCB)和十八烷基(C18)。然而对于不同类型的样品基质,通常需要组合多种吸附剂,没有吸附专一性。因此,根据茶叶中主要的基质成分,开发针对茶叶基质的特异性吸附材料,在提高净化效率方面具有重要意义。
金属有机骨架(MOF)作为近年来新兴的吸附材料,具有比表面积大,孔径可调谐等性质,在分离领域显示出了广阔的前景[11],对色素、染料等化合物展现出优异的吸附性能[12]。硼亲和材料(BA)是一种可以选择性分离富集顺式二羟基生物分子的功能性材料,硼酸配体可以可逆地与顺式二羟基结构化合物(如糖蛋白、糖类、核苷酸等活性成分)相结合,在食品检测、生物分离等方面应用广泛。茶多酚含有大量顺式二羟基结构[13],可通过硼亲和材料选择性地分离富集[14]。开发具有硼酸亲和基团的MOF材料,对于茶多酚等分子的吸附分离具有重要的意义。近年来,通过引入配体片段(5-硼苯-1,3-二羧酸(BBDC))方式协同参与功能性MOF的合成,引起了较大的关注。Gu等[15]采用一种简便的金属-配体-片段共组装方法来制备具有硼酸官能化的Cr(Ⅲ)基MOF,所得的MOF纳米颗粒在分离顺式二醇结构的生物分子方面展现出优异的效果,为功能化MOF的制备提供了一种简便而有效的方法。但是,由于MOF颗粒尺寸较小,在固液分离或过滤过程中处理困难,且易于泄露。此外,MOF材料中使用重金属(例如Cr(Ⅲ))具有高毒性,对环境造成潜在污染[16],因此,使用低毒的过渡金属(例如Zn(Ⅱ)),采用引入配体片段的策略制备功能性MOF吸附材料,在复杂样品的前处理分离中将具有重要的应用价值。
在这项研究中,我们将Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子与具有高吸附性能的锌基MOF结构相结合,同时引入硼酸配体,成功构建硼酸官能化金属-有机骨架磁性纳米复合材料(Fe3O4@BA-MOF),将其应用于茶叶农药残留检测过程中茶多酚等基质的特异性净化吸附。对复合材料吸附条件进行优化后,结合气相色谱-质谱联用技术,建立了一种茶叶样品中农药残留的有效分析方法。
1 实验部分
1.1 仪器、试剂与材料
Persee TU-1901紫外分光光度计(北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司); JEM-7800F扫描电子显微镜(JEOL,日本); LC-20A型HPLC系统(Shimadzu,日本); 8890A-5977B气相色谱-质谱联用仪(Agilent,美国); FTIR-Nicolet iS50傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Thermo fisher,美国); X射线粉末衍射仪(PANalytical,德国)。
六水合氯化铁、乙酸钠、己二醇、聚乙二醇、N,N'-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)、对苯二甲酸、5-硼苯-1,3-二羧(分析纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司);弗罗里硅土(Florisil)、乙二胺-N-丙基硅烷(PSA)(上海麦克林生化科技有限公司);纯净水(杭州娃哈哈集团有限公司);乙腈、甲醇(色谱纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司);农药混合标准溶液(包括4-溴-3,5-二甲苯基-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯-1(4-bromo-3,5-dimethylphenyl-N-methylcarbamate-1)、三正丁基磷酸盐(tri-iso-butyl phosphate)、蔬果磷(dioxabenzofos)、脱乙基另丁津(desethyl-sebuthylazine)、合成麝香(musk ambrette)、麦穗灵(fuberidazole)、2-甲-4-氯丁氧乙基酯(2-methyl-4-chlorobutoxyethyl ester)、灭菌磷(ditalimfos)、威菌磷(triamiphos)及苄呋菊酯(resmethrin),纯度99%,上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司);绿茶(大连市家乐福超市)。
1.2 Fe3O4@BA-MOF纳米复合材料的制备
1.2.1 Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子的制备
根据文献[17],采用经典水热合成法制备Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子。首先将六水合氯化铁(1.35 g)溶解在40 mL己二醇中,形成澄清的橙黄色溶液;然后向上述溶液中添加3.6 g无水乙酸钠和1.0 g聚乙二醇,将混合物剧烈搅拌30 min,并密封在反应釜中,在200 ℃下反应10 h,得到Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子。通过磁铁收集反应得到的Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子,分别使用超纯水及乙醇反复洗涤样品后,置于真空干燥箱中进行真空干燥。
1.2.2 Fe3O4@BA-MOF纳米复合材料的制备
根据文献[18],将0.05 g Fe3O4与3.0 g六水合硝酸锌混合于15 mL DMF试剂中,常温搅拌4 h。随后将配体对苯二甲酸(45 mg)及5-硼酸-1,3-二羧酸(4.5 mg)加入体系中。将混合物搅拌30 min后加入反应釜中,密封,120 ℃水热反应6 h。使用磁铁收集反应得到的Fe3O4@BA-MOF纳米复合材料,分别使用超纯水及乙醇反复洗涤样品后,置于真空干燥箱中进行真空干燥。
1.3 样品前处理
将茶叶样品研磨成粉末,混匀后称取10 g加入50 mL离心管中,加入30 mL去离子水(60 ℃)超声提取30 min。然后将混合物以4000 r/min离心20 min。收集上清液,作为茶叶提取液,用于后续净化处理。
1.4 茶叶中基质的磁性吸附及净化
称取50 mg的Fe3O4@BA-MOF,加入2 mL茶叶提取液,调节pH至7.0。振荡10 min后,通过外部磁铁将吸附材料吸引至管壁,吸取管中澄清液体。加入0.5 mL乙腈提取溶液中的农药,振荡30 s后加入无水硫酸镁(500 mg), 3000 r/min离心后取有机相进行气相色谱-质谱联用分析。
1.5 茶多酚的检测条件
1.6 农药的气相色谱-质谱检测条件
色谱柱:HP-5(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm, Agilent,美国)石英毛细管柱。色谱柱温度程序:40 ℃保持1 min,以30 ℃/min升温至130 ℃,然后以5 ℃/min升温至250 ℃,再以10 ℃/min升温至300 ℃,保持5 min;进样口温度:290 ℃;进样量:1 μL;电子轰击源:70 eV;离子源温度:230 ℃;传输线温度:280 ℃;采用选择离子监测模式(SIM)扫描。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Fe3O4@BA-MOF纳米复合材料的制备
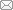
图1
图1
Fe3O4和Fe3O4@BA-MOF的表征结果
Fig. 1
Characterization results for Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@BA-MOF
a. scanning electron micrograph of Fe3O4; b. scanning electron micrograph of Fe3O4@BA-MOF; c. FTIR spectrum; d. X-ray diffraction pattern.
2.2 Fe3O4@BA-MOF吸附性能
如图2a所示,将Fe3O4@BA-MOF吸附材料加入茶叶提取液后,溶液中茶多酚含量迅速降低,在5 min内减少74.58%。随着吸附时间的延长,逐渐达到平衡,在20 min内Fe3O4@BA-MOF对茶多酚的吸附效果达到78.78%。
图2
图2
(a)吸附时间、(b)溶液pH、(c)吸附剂添加量对茶多酚的吸附效率影响(n=3)
Fig. 2
Effects of (a) adsorption time, (b) solution pH, and (c) adsorbent addition on the adsorption efficiency of tea polyphenols (n=3)
a. pH 7.0, adsorbent addition 50 mg; b. adsorption time 5 min, adsorbent addition 100 mg; c. pH 7.0, adsorption time 5 min.
综上,确定Fe3O4@BA-MOF的吸附条件为吸附时间5 min,溶液pH为7.0,吸附剂添加量为50 mg,并在此条件下进行后续实验。
2.3 重复使用性
作为色谱分离中的经典材料,硼酸亲和材料可通过溶液pH值,控制硼酸配体与顺式二醇化合物之间可逆的共价相互作用,实现目标物的“捕获和释放”过程[25]。在碱性条件下选择性捕获顺式二醇化合物,形成硼酸酯结构络合物,而在酸性条件下自动解离[26]。利用硼酸亲和材料的pH响应性,我们通过使用0.1 mol/L NaOH及HCl调节溶液pH,在pH 6.0的条件下对Fe3O4@BA-MOF中吸附的茶多酚进行解吸。通过4个连续的吸附再生循环对Fe3O4@BA-MOF进行评估,与初始值相比,经过4个循环后,Fe3O4@BA-MOF对茶多酚的吸附效率仅降低了2.57%,少量的损失可能归因于循环过程中特异性结合位点的减少以及基质中色素在MOF晶体结构中的孔隙填充[27]。总的来说,Fe3O4@BA-MOF在4个循环中具有良好的再生能力。
2.4 与商品化吸附材料的效果对比
在茶叶的前处理方法中,Florisil及PSA作为经典的吸附材料,广泛应用于茶叶中色素、有机酸等基质的吸附处理[24]。实验考察了Fe3O4@BA-MOF与Florisil、PSA对茶多酚的吸附效果差异。称取相同质量的吸附材料,置于茶叶提取液中,充分振荡后,离心分离基质净化液,使用分光光度计测定溶液中茶多酚的含量。结果表明,Fe3O4@BA-MOF、Florisil及PSA对茶多酚的吸附效率分别是78.78%、57.97%及77.34%。作为正相吸附剂,弗罗里硅土在茶多酚的吸附方面缺乏特异性[28],造成吸附效率较低。Fe3O4@BA-MOF与商品化PSA吸附剂对茶多酚去除效率相当,证明其在茶叶基质净化方面具有一定的实用性。
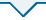
图3
图3
茶叶提取液经由Fe3O4@BA-MOF处理前后的 (a)高效液相色谱图及(b,c)磁分离照片
Fig. 3
Comparison of (a) HPLC chromatograms and (b,c) magnetic separation photographs of tea extract before and after treatment with Fe3O4@BA-MOF
2.5 Fe3O4@BA-MOF在茶叶农残检测中的应用
在实际样品的气相色谱分析中,基质中的热敏性分析物可能会在仪器衬管和色谱柱的活性位点分解,导致峰形失真。同时,共提取物会与目标农药竞争进样口或柱头的金属离子、硅烷基等活性位点,导致色谱信号增强[29]。因此,研究开发针对样品基质的吸附材料,对实际应用中农药残留量的检测具有重要意义。取茶叶空白样品,经过前处理吸附净化后(依照1.3、1.4节方法)得到空白基质溶液。以空白基质溶液稀释农药混合标准溶液(根据文献[30]选择10种茶叶中常见的农药),配制成基质混合标准溶液,通过气相色谱-质谱联用仪进行检测。以目标物的峰面积(y)对质量浓度(x)进行线性回归分析,在1~10 mg/L的线性范围内,测得混合标准溶液中各农药的线性良好。以信噪比(S/N)=3确定10种农药的检出限(LOD),以S/N=10确定10种农药的定量限(LOQ)(见表1)。
表1 10种农药的线性方程、质谱参数及检出限
Table 1
| Target | Retention time/ min | Quantitative ion (m/z) | Qualitative ions (m/z) | Linear equation | LOD/ (mg/L) | LOQ/ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDMC-1 | 20.82 | 200 | 202, 201 | y=2565.75x-1098.68 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| Tri-iso-butyl phosphate | 10.25 | 155 | 139, 211 | y=4212.41x-949.99 | 0.05 | 0.15 |
| Dioxabenzofos | 13.09 | 173 | 158, 145 | y=7505.16x-2727.13 | 0.06 | 0.20 |
| Desethyl-sebuthylazine | 14.72 | 172 | 174, 186 | y=14137.27x-2782.72 | 0.06 | 0.20 |
| Musk ambrette | 16.27 | 253 | 268, 223 | y=5244.07x-2961.27 | 0.10 | 0.30 |
| Fuberidazole | 17.37 | 184 | 155, 129 | y=11082.79x-2776.89 | 0.10 | 0.30 |
| MCPA-butoxyethyl ester | 20.82 | 300 | 200, 182 | y=3405.81x-1459.83 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| Ditalimfos | 21.86 | 130 | 148, 299 | y=1678.82x+337.74 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| Triamiphos | 24.81 | 160 | 294, 251 | y=6048.10x-426.68 | 0.06 | 0.20 |
| Resmethrin | 26.41 | 171 | 143, 338 | y=4967.23x-3187.67 | 0.06 | 0.20 |
y: peak area; x: mass concentration, mg/L.
在阴性茶叶样品中添加一定浓度的农药混合标准溶液,依照1.3、1.4节方法进行样品前处理,然后进行GC-MS分析。结果如表2所示,10种农药的平均加标回收率为75.8%~138.6%, RSD为0.5%~18.7% (n=3),表明该方法适用于茶叶中农药的检测分析。
表2 10种农药加标回收率及精密度(n=3)
Table 2
| Target | Spiked/ μg | Found/ μg | Recovery/ % | RSD/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDMC-1 | 3 | 2.82 | 94.3 | 16.3 |
| 1 | 1.27 | 127.2 | 4.4 | |
| Tri-iso-butyl phosphate | 3 | 2.82 | 93.9 | 12.6 |
| 1 | 1.09 | 109.1 | 7.5 | |
| Dioxabenzofos | 3 | 3.07 | 102.4 | 3.2 |
| 1 | 0.92 | 91.2 | 0.6 | |
| Desethyl-sebuthylazine | 3 | 2.48 | 82.8 | 6.2 |
| 1 | 1.03 | 103.4 | 2.5 | |
| Musk ambrette | 3 | 2.28 | 75.8 | 10.6 |
| 1 | 1.27 | 126.7 | 0.5 | |
| Fuberidazole | 3 | 2.28 | 75.7 | 6.4 |
| 1 | 0.89 | 89.0 | 4.8 | |
| MCPA-butoxyethyl ester | 3 | 2.82 | 94.0 | 12.8 |
| 1 | 1.16 | 116.4 | 1.4 | |
| Ditalimfos | 3 | 2.85 | 94.9 | 9.5 |
| 1 | 0.88 | 88.7 | 8.9 | |
| Triamiphos | 3 | 3.54 | 118.3 | 10.3 |
| 1 | 1.32 | 131.6 | 10.0 | |
| Resmethrin | 3 | 3.06 | 102.5 | 18.7 |
| 1 | 1.38 | 138.6 | 0.7 |
3 结论
本研究针对茶叶农药残留检测中前处理复杂等问题,制备了一种特异吸附茶叶基质的磁性固相萃取吸附剂Fe3O4@BA-MOF。结合气相色谱-质谱,建立了一种有效测定茶叶中农药的方法。磁性纳米粒子与锌基MOF结构相结合,将硼酸配体引入MOF结构中,针对茶多酚等基质成分具有吸附特异性,制备方法简单,可以有效简化样品前处理步骤。本方法在针对茶叶中农药残留分析方面具有较高的应用价值和广阔的应用前景,但对于茶叶基质中咖啡碱、有机酸等成分消除能力较弱,仍需要进一步的探索研究。
参考文献
The ferrofluid phase was prepared according to mixing magnetic nanoparticle and the hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent as a green microextraction solvent. This new composite was applied for vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (VA-HDES-ferrofluid-DLLME) of doxycycline (DOC) residual extraction and determined through high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (HPLC-UV). The characterization of magnetic nanoparticle was investigated by XRD, TEM and FESEM. The dependency of DOC microextraction to main variables and their interaction and find optimum points were undertaken using response surface methodology with either central composite design (CCD). Thus, the optimum pH, ionic strength, ferrofluid volume and vortex time for DOC extraction are determined to be 3.0, 4%w/v, 150 μL and 7 min, respectively. According to this condition, linear response is found to be greater than 10-400 ng mL, with a correlation coefficient of 0.983. The detection and quantification limits are 3.6 and 8.5 ng mL, while the repeatability and reproducibility as precision criteria (RSD%) are 3.74% and 4.15%, respectively. The DOC recoveries in all of the urine, blood plasma and milk samples are between 86.70 and 97.48%, with RSD% lower than 5.72%.Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Tea is a widely consumed beverage and has many important physiological properties and potential health benefits. In this study, a novel method based on supercritical fluid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (SFC-MS) was developed to simultaneously determine 11 amino acids in different types of tea (green teas, Oolong tea, black tea and Pu-erh tea). The separation conditions for the analysis of the selected amino acids including the column type, temperature and backpressure as well as the type of additive, were carefully optimized. The best separation of the 11 amino acids was obtained by adding water (5%, v/v) and trifluoroacetic acid (0.4%, v/v) to the organic modifier (methanol). Finally, the developed SFC-MS method was fully validated and successfully applied to the determination of these amino acids in six different tea samples. Good linearity ( ≥ 0.993), precision (RSDs ≤ 2.99%), accuracy (91.95%-107.09%) as well as good sample stability were observed. The limits of detection ranged from 1.42 to 14.69 ng/mL, while the limits of quantification were between 4.53 and 47.0 ng/mL. The results indicate that the contents of the 11 amino acids in the six different tea samples are greatly influenced by the degree of fermentation. The proposed SFC-MS method shows a great potential for further investigation of tea varieties.
For the first time, a new kind of bionic multi-tentacled ionic liquid-modified silica gel was synthesized and used as selective adsorbent in the preparative separation of tea polyphenols (TP) from green tea leaves. It was found that silica particles with polyvinyl alcohol chains modified by N-methyl imidazole proline salt (PVA·Im·Pro@SiO) had the excellent performance in selective adsorption as well as fine separation for target compounds. The new adsorbent exhibited high adsorption capacity and good reusability, meanwhile the antioxidant activity of TP could be improved through its efficient enrichment. It properties and adsorption mechanism were also investigated comprehensively and compared with those reported sorbents. Finally, the preparative separation of individual catechin from crude extracts was successfully achieved on the chromatographic column packed with PVA·Im·Pro@SiO particles and four main constituents were obtained successively. The study was expected to provide a new way for the effective separation of similar bioactive compounds.Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
The selective recognition, isolation, and subsequent enrichment of target glycoproteins are becoming more and more important in clinical diagnosis. In this work, nano-sized molecularly imprinted polymers integrated double affinity (i.e. metal ion affinity and boronate affinity) (D-MIPs) were prepared for specific separation of ovalbumin (OVA). Poly(styrene-glycidyl methacrylate) nanoparticles (PSG) with epoxy bonds were firstly grafted with iminodiacetic acid (IDA) by ring-opening reaction, and then the Cu2+ was chelated to prepare PSG/IDA-Cu2+. Subsequently, imprinted OVA molecules were pre-immobilized through Cu2+ ion affinity. Finally, a surface imprinting layer was formed though the gentle self-oxidization of a kind of boronic acid ligand (i.e. 3-aminophenylboronic acid, APBA). By washing out imprinted molecules, as-prepared D-MIPs posed higher monolayer binding capacity (138.92 mg g(-1)) and faster capture kinetics (30 min) for OVA, when compared with single affinity integrated MIPs (S-MIPs) and non-imprinted polymers (NIPs), and the chemical adsorption dominated double affinity was the rate-determining step for whole adsorption process. The imprinting factor (IF) of OVA, horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) by the available D-MIPs were 4.44, 2.23 and 1.47, respectively, which confirmed the better selectivity for OVA. D-MIPs performed favorable regeneration ability and a promising application in actual sample. In addition, a combination of synergistic multiple bindings and imprinting effect, as the mechanism for enhancing specific separation, was also demonstrated.